Structuring Financial Modeling Workshops for Real Estate and Infrastructure Projects
Introduction to Real Estate Modeling Certification Program
The capital and infrastructure projects are long term and extremely reliant on accurate financial projections. Investors, corporate finance teams, developers and investors use sound financial models to determine feasibility, risk analysis and organize financing arrangements. Financial modeling skill has already
become a strategic asset, and not a technical ability, in a business environment where interest rates are variable, construction costs change at a very fast rate and regulatory frameworks are subject to change.
Organising effective financial modeling workshops will be done in a way that the attendees get not just to learn how to use spreadsheet but above all how to make the judgment and analytical discipline including scenario thinking as demanded by the major real asset investments. These workshops should not be just formula and template but they should be reflective of what is going on in the real world in that deal process and they should incorporate industry specific assumptions and they should also teach the participants how to analyze a project in the manner that professional investors analyze the same.
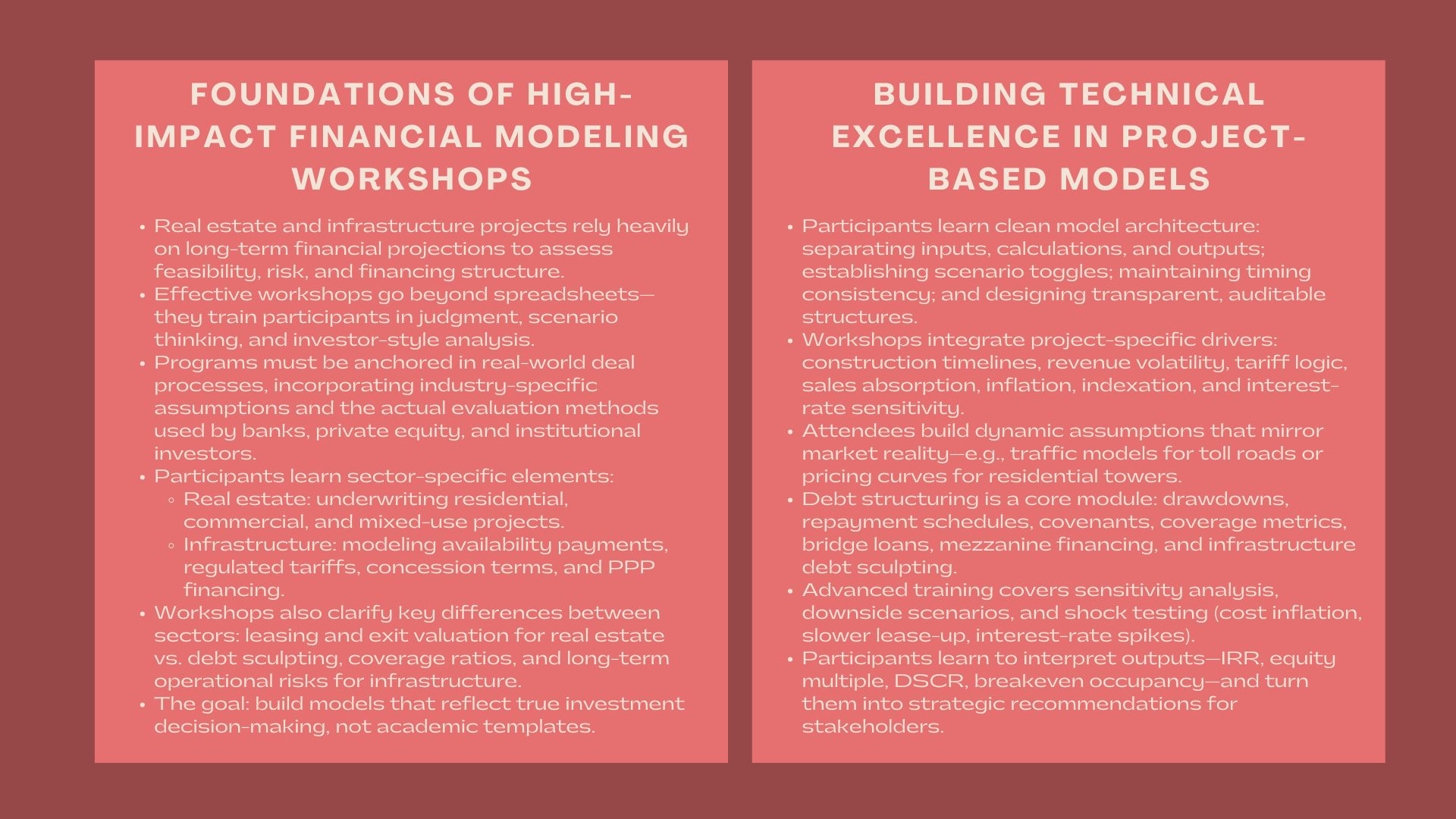
1. Bases of High-Impact Training Design.
1.1 Correlating the Workshop with Investment Requirements in the Real World.
An organized workshop sets in place with an understanding of the actual evaluation process of real estate and infrastructure deals. These assets are priced using long-term cash flows that could be dependent on the occupancy, tariff contracts, user demand, or concession contracts unlike corporate valuation. Thus, the training should be based on the realistic context of investment.
In the case of real estate, the participants learn the underwriting principles of residential, commercial, and mixed-use development projects. In the case of infrastructure the emphasis is on controlled assets, availability-based revenue systems and financing of public- private partnerships. The fact that the workshop is anchored on specific industry settings will lead to the participants coming up with models which will simulate the way banks, private equity firms and institutional investors carry out due diligence.
1.2 Differentiating between Real estate and Infrastructure Modeling.
Despite similarities in the fact that both sectors are based on the discounted cash flow analysis, the assumptions are quite different. Real estate models are centred on leasing, building schedules, operation costs, and the valuation on exit. Capital structure, coverage ratios, debt sculpting, and long-term operational risks, however, assume great importance in the models of infrastructure.
Participants of a workshop should learn how to differentiate these structures, how to adjust assumptions, and how to apply the appropriate technical tools in the support of each project class. It is here that the real estate and infrastructure financial modeling and structuring course becomes a practical bridge between academic knowledge and real-world investment requirements.
2. Building Technical Excellence in Project-Based Financial Models
2.1 Designing Clean, Transparent, and Auditable Model Architecture
An essential element of the workshop is that of model architecture- of logic flow, modularity, traceability and error-proof structure. The participants are taught to create the models that are simple to adjust, audit, and report to the investors. The training focuses on the separation of inputs, calculations and outputs; construction of a scenario fetch switch and consistency of timing conventions.
The construction of real estate development illustrates the way to organize the construction plan, rate of absorption and phases. Examples of infrastructure display the organization of capital expenditure profiles, life cycle, concession terms and long term maintenance cycles.
2.2 The incorporation of Project-Specific Drivers and Risk Variables.
The variables that determine the project feasibility include costs, timelines, revenue volatility, financing costs and macroeconomic conditions. During the workshop, the participants construct assumptions that reflect the reality of the market. An example of this is that modeling a toll road would need traffic sensitivity/tariff escalation logic and modeling a residential tower would need pricing levels and sales absorption curves.
The workshop equips a participant with knowledge on how to make predictions on revenues and expenses that are realistic, work with past tendencies as proxies, and benchmarking using industry standards. They get to know how to integrate the inflation, indexation, fluctuations in interest rates, and foreign exchange exposure particularly relevant to cross-border investors.
2.3 Building Debt Schedules and Finance Structures of a Project.
A significant number of real estate and infrastructure developments depend on leverage in order to increase returns. As such, participants construct comprehensive debt schedules comprising of drawdown schedules, repayment vehicles, covenants and covering metrics by lenders.
The workshop proposes debt sculpting in infrastructure cases, which involves the formulation of debt repayment sequences that match cash flows of projects. Bridge loans, construction financing and mezzanine layers are common structures found in the real estate. The participants examine the impact of leverage on equity returns and financial covenant on feasibility.
3. Training Advanced analytical and strategic skills.
3.1 Investment decision Scenario and Sensitivity Testing.
Anticipation of uncertainty is one of the most important skills in the real asset modeling. An intensive workshop is designed to teach attendees how to develop sensitivity tables, downside cases and scenario toggles which reproduce market shocks as well as project-specific obstacles.
Throughout, an example of a participant testing is to test what happens when the cost of construction increases by 15 percent, lease-up periods are doubled or the interest rate increases prior to stabilization. These activities build investment intuition – enabling participants to know which assumptions are of most importance and the ways of instilling resilience to project structures.
3.2 Strategic Implications of Model Results.
The role of a financial model is not to calculate, but make decisions. Thus, the workshop will inform the participants on how to analyze the outputs of IRR, equity multiple, net cash flows, DSCR, breakeven occupancy, or refinancing potential.
These outputs are converted into actionable insights with the help of case studies:
– Is the developer phase to be constructed to reduce capital intensity?
– Does a price-taker EPC contract limit the risks to construction?
– Is it possible to re-gear using new financing once it gets stable?
The training transforms the mindsets of the participants who are model builders to the level of investment thinkers by translating the financial results to strategic recommendations.
3.3 Reporting the findings to shareholders, financiers and boards.
Organized workshop also comprises training in communication skills. Models have to be reformed into investor presentations, credit memos and internal investment papers.
The participants will be taught to build stories using charts, essential metrics, and risk summaries. They train on the articulation of the investment story: project reasons, financial prowess, sensitivity results, and risk elimination plans. The capability is necessary to developers, corporate finance teams, and investment managers who want to get funding or get approvals.
4. Creating Workshops that Reflect Professional Investment Space.
4.1 Blending Theory, Hands-On Modeling and Case Simulations.
Best training programs mix between training, practical activities and simulated real cases. The participants construct models by hand, audit constructed models, and determine real deal analysis. This combination style is sufficient to guarantee thorough learning and practice.
The project-based financial modeling workshop for developers and investors often integrates capital markets insights, due-diligence techniques, and investor return expectations. All these realistic surroundings enable participants to learn about how professional deal teams are managed and decisions made.
4.2 Comparing with real Data and Industry Benchmarks.
To be up-to-date, workshops consider actual data: construction costs per industry, regional rental yield and infrastructure capital intensity indicators and project finance spreads. Through benchmarking model assumptions against actual benchmarks, participants can be taught to come up with believable investment cases and not make impractical projections.
4.3 Content Modification to suit various teams and competencies.
The participants do not always have the same background. Others are engineering and operations, finance and investment management. Thus, the workshops should be flexible and include easy to use modules and advanced and deal-specific parts to attract both beginners and experts in the field.
This tailoraiding is necessary so that the cross functional teams comprising developers, analysts, financial controllers, and project managers are able to have a common idea of how to identify and organize real assets investments.
Conclusion
In the ongoing growth of the economy and corporate expansion, financial modeling capability is a strategic requirement, as real estate and infrastructure investments are the drivers of economic growth and corporate expansion. Professionally organized workshops provide the technical expertise, analysis and judgement expertise, which allows professionals to assess, fund and manage complex initiatives. Training programs will help participants to work with confidence in high-stakes investment environments by combining industry-specific assumptions, the real project simulations and serious scenario analysis.
Those organizations making such investments in such workshops either with a real estate and infrastructure financial modelling and structuring course or with a project-focused financial modelling workshop on the part of developers and investors develop greater internal resources and are placed in a position to reap the benefits of core real assets in years to come.