Operational Risk and Compliance Training for Corporate Banking Teams
Introduction to Advanced Operational Risk and Compliance Course
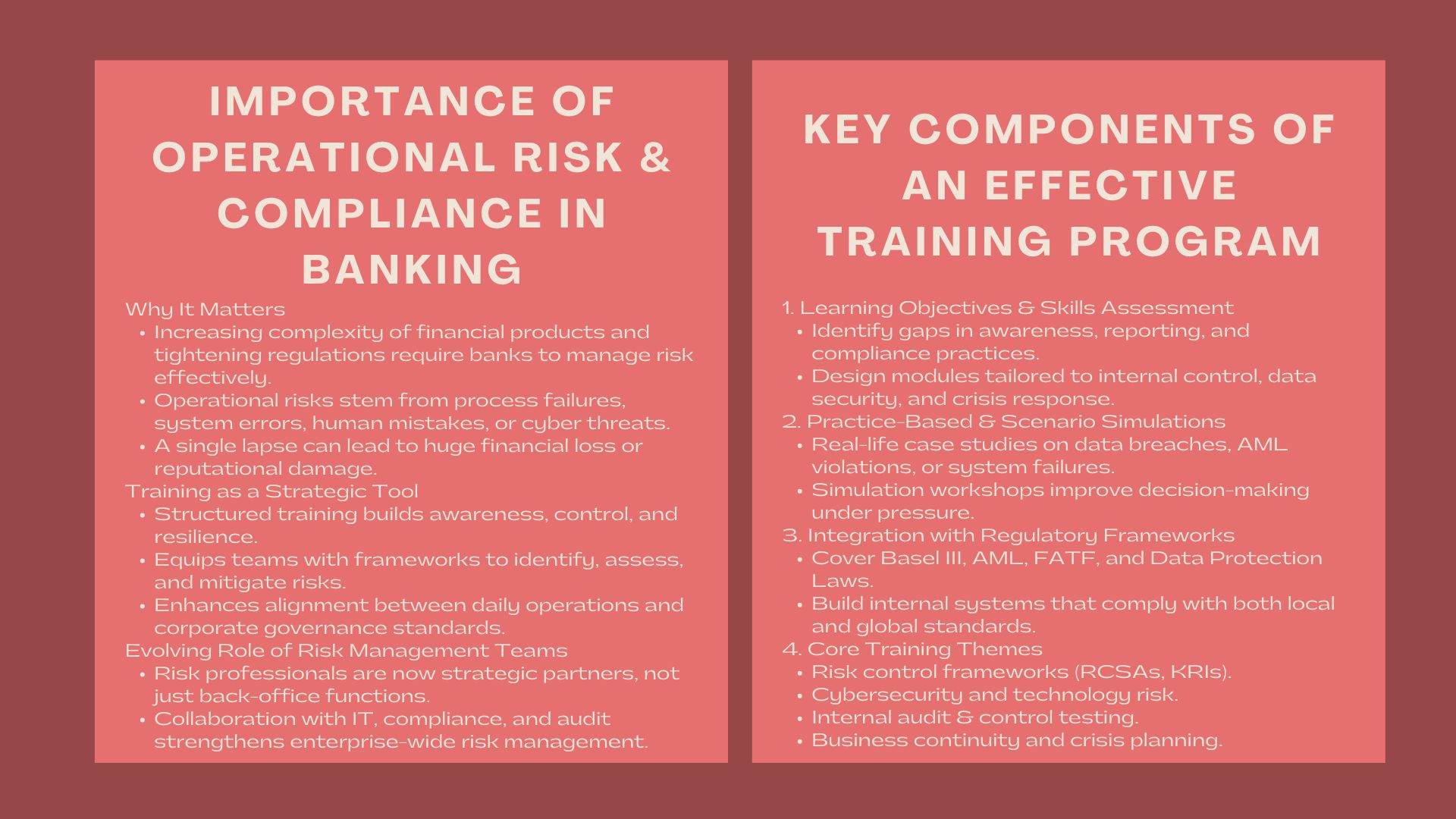
In current banking, operational risk and compliance management have become important ingredients of good governance and sustainable performance. As more financial products are becoming complex, regulatory oversight is escalating, and technology is changing too fast, corporate banking departments are required to know how to recognize, handle, and reduce operational risks to a manageable level.
Structured training programs are essential in an environment where a lapse might lead to huge financial losses or reputational losses. Such programs provide the professionals with the frameworks and tools that they would need to ensure internal controls are reinforced, compliance practices enhanced, and the resilience against future disruptions developed.
This paper discusses the main points connected to the design and execution of an effective operational risk and compliance training program among corporate banking professionals with respect to skills building, real-life applications, and quantifiable business results.
The Value of Operational risk management in Banking.
Operational Risk: What it is and why it matters.
Operational risk is a term that describes the possibility of losses due to ineffective processes, system-failure, human error or external occurrences. Operational risk is unlike credit or market risks because it occurs in all the departments of a bank- customer service and IT infrastructure to transaction processing and compliance.
The increased use of the online platform has exposed financial institutions to cyberattacks, data breaches, and system outages. Operational risk is now part of the overall risk management strategy of a bank and it therefore is no longer confined to the back-office operations.
The Disability of Poor Risk Controls.
Uncontrolled operational risks may result in regulatory fines, loss of money, and reputation. Unauthorized trading, internal fraud, and lack of compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) requirements are some of the incidents that may seriously damage customer trust.
Through structured operational risk management training Phnom Penh, corporate banking teams gain the ability to assess exposure, implement control mechanisms, and respond swiftly to risk events. Training also assists the staff to ensure that daily operations are aligned to the overall risk appetite and compliance structures of the institution.
The Changing Position of Risk Management Teams.
Risk management is not considered as another support role today, it is an inseparable element of business strategy. Banking professionals are supposed to anticipate and analyze the emerging risks, such as the ones related to new technologies, partnering with new third parties, sustainability reporting, etc.
The operational risk professionals currently collaborate closely with compliance, audit, and IT departments to make sure that the risk management is comprehensive. To ensure resilience in the highly volatile regulatory environment, training programs that facilitate this mutual cooperation between the functions are necessary.
Creating Efficient Operational Risk Training Courses.
Determining Learning Objectives and Gaps in Skills.
According to the banks, prior to the creation of a training curriculum, they are to evaluate the levels of skills within departments. Key questions include:
- Are the employees aware of the operational risk structure of the bank?
- Is identification and reporting of risks standardized?
- Are compliance violations being tracked and amplified successfully?
By understanding these gaps, an institution can lead a tailored program that can address the key issues that are highly relevant at a given point in time either to enhance internal controls, data security, or incident response among others.
Creating Practice-Based and Scenario-Based Modules.
Training must not be limited to theoretical but must include real life examples and case studies. Simulations and scenario analysis provide the participants with the knowledge of implementing risk management techniques. As an example, workshops could entail a response to a simulated data breach, root-cause analysis to an operational failure, or risk analysis of a new financial product.
Simulation games enhance decision making during a crisis and stimulate proactive risk thinking vital to high stakes corporates.
Combining Compliance and Regulatory Frameworks.
The contemporary operational risk management is very much interwoven with compliance regulations. Basel III, anti-money laundering regulations, and data protection laws are some of the frameworks that the financial institutions are bound to follow. Comprehensive programs like banking compliance workshops Phnom Penh train professionals to interpret and apply these standards effectively in daily operations.
Participants are taught how to come up with internal control systems that are in line with international and local requirements of compliance, which will lower chances of regulatory breaches and fines.
Basic Themes in Risk and Compliance Training.
Frameworks and Controls of Operational Risk.
This module presents the most important principles of risk governance, such as risk identification, assessment, mitigation, and reporting. The participants are taught how to develop risk control self-assessment (RCSAs), key risk indicator (KRIs), and incident management systems.
Internal Audit and Control Testing.
Audit principles training assists the banking professional to analyze the efficiency of the established controls. It makes sure that this problem is identified early and remedial initiatives are taken in due time.
Technology Risk and Cybersecurity.
Cyber threats are a significant threat to operations with the introduction of digital banking. The cybersecurity awareness, access control, and data protection modules enable employees to protect the important assets in terms of information.
Anti-Money laundering/Regulatory Compliance.
The compliance-oriented sessions will educate the professionals on how to identify suspicious transactions, conduct due diligence, and comply with the international standards such as the FATF and the AMLD.
Crisis Management and Business Continuity Planning.
The banking operations can be crippled by operational disruptions brought about by cyber attacks, system failures, or natural calamities. Business continuity planning and strategies to address crisis communication should also be regarded as a part of the training program to provide resiliency in business operations.
Presentation and Measurement of the Training Program.
Learning Methods: Blended Learning.
Combination of classroom workshops with e-learning modules and on the job mentoring is the best program to use. This is the best strategy as it supports different styles of learning and maintains a uniform knowledge transfer among the departments.
Digital learning platforms provide employees with the ability to study materials online, complete quizzes, and study the most important issues independently. Live workshops on the other hand promote interactive discussions and joint problem solving.
Chief Domain of Trainers and Subject Matter Experts.
The use of experienced trainers (particularly trainers who have experience in risk management, internal audit or regulatory compliance) will make the training programs more credible and relevant. They are in a position to give first hand experiences on the actual challenges that banks are going through and give the best practices as experienced by the banks throughout the region.
Measuring Effectiveness
The effectiveness of a risk management training program can be evaluated by the use of well-defined performance indicators, including:
- Less compliance breach or audit programs.
- Reducing response and resolution times.
- Better employee confidence to deal with operational risks.
- Improved regulative feedback or audit report.
Post-training tests, surveys, and on the job can be used to identify whether the participants are putting their knowledge into practical use.
Advantages of Operational Risk and Compliance Training.
Strengthened Risk Culture
Risk awareness and responsibility is a culture that is developed through training programs. Employees are made to understand that risk management is not the prerogative of compliance department. This common mentality promotes initiative in solving problems and openness.
Less Financial and Reputational Exposure.
When banks invest in organised training, they are in a better position of identifying and averting problems before they begin to spiral. This does not only save the financial performance but also save the brand reputation in a highly competitive market.
Increased Regulatory Confidence.
Continuous training by regulators is considered as a good governance. Regular compliance education is more likely to improve the trustworthiness and credibility of the institutions during inspections and audits.
Better Operational Efficiency.
Risk processes and controls allow employees to be aware of the inefficiencies, streamline their process, and eliminate redundancies. The outcome is a faster-paced organization that is able to adjust to regulatory and market changes.
New Trends in Risk and Compliance Training.
Technology based learning is the future of risk management training. Risk scenarios are predicted and modelled more accurately with the assistance of artificial intelligence (AI), data analytics, and interactive simulations.
Virtual workshops and computerized compliance dashboards are also becoming a trend, and banking teams can now check and report operational risks on a real-time basis. With sustainability reporting and ESG existing as a component of regulatory architectures, compliance training will only continue to adapt to illustrate new spheres of control.
Conclusion
One of the pillars of proper corporate governance is operational risk and compliance training. Financial institutions can protect their operations and gain the trust of stakeholders by providing the banking professionals with the knowledge, tools, and structures of identifying and mitigating risks.
In a more and more complicated financial environment, lifelong learning keeps corporate banking teams strong, responsible, and ready to take up new challenges. Organizations that invest in performed, practical and futuristic training programs will not only improve performance, they will also ensure a sustainable competitive advantage in the dynamic international market.